Class Information
AP Physics Class

Resources

Physics News
read more
AP Physics - Mr. McMullen
AP Physics B
Free-Response Index
For explicit use of students at JPS
|
|
B1 |
B2 |
B3 |
B4 |
B5 |
B6 |
B7 |
|
|
Collisions |
Springs &
Energy |
Current
balance |
Fluids &
projectiles |
Thermo
cycle |
Mirror – ray diagrams |
deBroglie
wavelength; photoelectric effect |
||
|
Momentum
conservation |
Mechanics;
springs |
LAB:
magnetic field measurement |
fluids |
Lens – ray
diagrams |
Thermo
cycle |
Nuclear
radiation |
||
|
Dynamics;
inclined plane |
Mass
spectrometer |
Circuits;
RC circuit |
Torricelli’s theorem |
Thermo;
isobaric process |
LAB:
determine the focal length of a lens |
Positron-electron pair annihilation |
||
|
dynamics |
q moving
thru a B field |
RC circuit |
Torricelli’s theorem |
Thermo;
isometric process |
LAB:
determine the index of refraction of a slab of glass |
Pair
production |
||
|
Dynamics;
modified Atwood’s w/ spring |
LAB:
World class runner – 100 m dash |
Electrostatics; field and potential |
Snell’s
Law; graphical derivation of n; Thin film
interference |
Thermo; PV
diagram |
Energy of
photon; wave properties of an electron |
|
||
|
LAB:
graphical derivation of g |
Energy,
momentum conservation; friction dynamics |
Electrostatics |
Reflection/refraction; Double
slit interf. |
Thermo; PV
diagram |
deBroglie
wavelength;
Electron/positron annilihation |
|
||
|
Kinematic,
dynamics & graphs |
pendulum |
Electrostatics – point charges |
LAB:
double slit interference |
buoyancy |
PV=nRT
graph |
Energy
levels;
Photoelectric effect |
||
|
Kinematics, dynamics, graphs |
pendulum |
Electrostatics – point charges |
LAB: two
source interference |
Fluid
flow: Torricelli’s theorem |
PV=nRT
graph |
Photons
and Photoelectric effect |
||
|
Energy
conservation, rollercoaster, circles |
Pressure
and depth; |
Faraday’s
Law |
Two source
interference |
PV-diagram, thermo |
LAB:
Photoelectric effect |
|
||
|
Energy
conservation, rollercoaster, circles |
Pressure
and depth; |
LAB:
Standing waves in tube |
Faraday’s
Law |
PV-diagram, thermo |
|
|
||
|
F = ma,
accel, FN, |
R and C in
circuit |
Rail Gun:
FB, work-energy |
LAB:
concave mirror image |
PV
diagram, energy |
Fluids:
pressure-depth, gauge pressure, Archimedes’s Princ. |
|
||
|
F = ma,
kinematics |
LAB:
circuit to power motor |
single &
double lens |
E in
capacitor, vector motion of electron, |
PV
diagram, energy |
Bernoulli’s princ., power, fluid flow |
Atomic
energy diagram, range of visible light |
||
|
|
|
Two light
bulbs, rated in |
|
|
LAB:
spring and Archimedes’ Principle |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
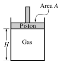
Canister
of gas: |
LAB:
deBroglie wavelengths, atomic energy diagrams |
||
|
2001 -
circular motion, projectile |
momentum,
projectile |
electrical forces, fields, potential |
wavelength dependent refraction |
LAB - temp
dependent resistor used as thermometer |
gas thermo
- types of processes. |
nuclear
reaction, mass defect. |
||
|
(2000) kinematics graph, projectile |
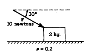
Incline,
forces, friction. |
RC
circuit. dielectric |
refraction, thin film. |
Photoelectric effect |
LAB:
determine specific heat of liquid. |
Elec, Mag
field on particle. Mass spectrometer. |
||
|
1999 –
kinematics, work, en, friction |
CRT,
electron projectile in E field. B field |
Energy on
hill, induction |
radioactive decay, half life |
centripetal force on a turntable |
Refraction and diffraction Lab experiments – design |
Gas
cycle, heat engine |
||
|
1998 –
acceleration on table, projectiles |
force on
charged particle in E field. |
LAB:
Energy transfer by GPE. Specific heat |
142 –
bulbs in circuit. Drawing, Ohms law. |
Standing
waves on a string. |
ball
swinging directions of V and a |
diff
grating interference, Bohr level. |
||
|
1997 – F
vs D – find work, etc. |
LAB:
Centripetal force |
Spring,
force on current in B field. |
use
resistors to heat water – draw circuit, do
calculations |
convex
lens, concave mirror, draw and calculate |
A –
discuss experiment, pick from 3. |
energy
levels |
||
|
1996 -
elastic and inelastic collision on air track |
LAB:
Hooke’s law |
Double
slit interference |
Hook up
specific circuit. Ohm’s law |
alpha
decay, energies, momentum |
Millikan
experiment |
gas in
a can, moles |
||
|
1995 –
air track, inelastic collision, energy in spring |
toaster
circuit, hooking up. |
Acceleration on a roller coaster. |
Energy
level diagram, de Broglie |
Heat
engine, Carnot efficiency, power |
resonance
in a tube. |
B force on
electron. |
||
|
1994 -
kick soccer ball over fence – proj. |
arc track,
energy ideas, friction work |
A:
photoelectric effect graph; B:
relativistic motion. |
work to
acc electrons, control by B field |
path of
light in water, TIR, lens under water. |
motional
emf, induced E, Lenz’s Law |
|
||
|
1993 –
elevator, constructing d, v, a graphs for motion |
E fields
& Potential of point charge |
control
chgd particle with B & E fields |
refraction in glass and l dependence |
gas
process, work and heat in cycle (mistake) |
X ray
tube, |
|
||
|
1992 –
vertical circle, tension, centripetal motion |
conservation of momentum, energy, during collision
and separation. |
elec
power, fusion, heat flow |
Energy
level diagram, transitions |
CRT, E, B, field on electron |
convex
lens, concave mirror, diagram & calc’s |
|
||
|
1991 –
monkey static equilibrium, centripetal accel |
control
of charge with E & B fields. |
Heat
engine, eff, heat absorption by water. |
battery,
get intern resistance, ohm’s law, draw circuit |
Nuclear
alpha decay, equation, de Broglie l, energy,
Rutherford scattering |
2 slit
interference, photoelectric work function |
|
||
|
1990 - inelastic collision projectile |
chg
particle doing projectile path betw charged plates |
ohm’s
law, power |
gas
cycle, work done, efficiency |
accelerated elect. Resulting e-m waves, energy |
reflection, refraction, thin film interference. |
|
||
|
1989
-Centripetal motion, projectile. |
electric
force, potential, work |
electrical – mechanical energy equivalence, Ohm |
Thermo –
PV diagram, work done in various processes |
Nuclear
decay, energy, rest mass. |
convex
lens, image formation, graph di vs do |
|
||
|
1988 -
helicopter vertical acceleration, tension,
kinematics |
ball
bounce, energy lost, specific heat. |
RC
circuit, beginning & end |
B field
of wire, force on moving charged particle |
refraction, crit angle, new medium |
Photoelectric effect, calculations |
|
||
|
Modified
Atwood’s machine |
forces,
field, potential of point charges. |
Heat
movement, specific heat |
Ohm’s
law, Q=It |
refraction, speed, critical angle |
Photoelectric effect, graphical calc |
|
||
|
1986 -
Atwood’s mach, tension, acceleration |
Energy in
spring, projectiles |
Circuits,
ohm’s law |
Induction, forces on wire in B field |
Carnot
cycle, PV diagram |
Concave
and convex lenses – diagrams and calculations. |
|
||
|
1985 –
ballistic pendulum |
static
equilibrium, acceleration on incline, energy conv |
e field,
work, energy, forces |
Specific
heat, flow, phase change. |
double
slit interference in air and water. |
energy
level transitions, photons |
|
||
|
1984 -
vertical circle, projectile |
momentum
cons, elastic coll. angles |
heating
water, change of state, time, ohm’s law, power. |
e – m
forces on chg part. |
refraction, thin film interference |
radioactive decay, half life, alpha |
|
||
|
1983 –
friction, F = ma, tipping |
inelast
coll, energy in spring, shm. |
ohms law,
circuit |
thermo
processes work |
concave
mirror |
Photoelectric effect, calculations of h, work
function . . . |
|
||
|
1982
(left) sprinter, kinematics graph. |
|
swing on
rope, tension at lowest point, energy |
Hookup of
clock and radio. |
flux,
induction |
convex
lens |
four
modern phys experiments – choose 1 and explain |
||
|
1981 –
friction, work, energy |
springs,
energy, momentum cons in explosion |
stat
equil of charged particle in electric field |
circuits
– power, ohm’s law |
convex
lenses, ray diagrams |
Energy
absorption, specific heat. |
|
||
|
1980 -
static equilibrium |
circuits
and connections |
photoelectric eff. Data and graph |
Using one graph, sketch its companion |
Nuclear
decay, cons of momentum, calc of energy |
kin
theory, press. |
|
||
|
1979 –
potential & Kinetic energy of projectile |
F = ma |
muons,
modern physics, relativity |
electric
& magnetic forces on charged particles |
gas laws,
p-v diagram, work |
refraction |
Charged
spheres, elec forces. |
||
|
Vertical
circular motion |
Projectile; inelastic collision |
capacitor |
Induced
emf |
Concave
mirror; ray diagram |
Photon
collision with mass |
Bohr
model; deBroglie wavelength |
||
|
1977
work-energy, kinematics |
centripetal force, banked road. |
e-m
forces, work, fields |
Ohm’s law,
power, spec ht, thermo |
Interference of sound waves. 2 pt sources |
Relativity
and modern physics – sketching graphs |
|
||
|
Elevator;
Atwood’s machine |
Cons of
momentum; bullet block combo |
circuits |
Mass
spectrometer |
Waterfall:
Grav pot energy converted to thermal energy |
Converging
lens Ray
diagram |
Photoelectric effect |
||
|
1975-friction, energy, kinematics |
electric
field, work |
Thermo
processes, gas laws |
single and
double slit interference |
energy
levels, transitions, photons |
electrical
work, centripetal motion, mass spectrometer. |
pendulum,
shm, energy, centripetal. |
||
|
Pendulum;
dynamics |
Electron
moving in a B field |
Converging
lens Ray
diagram |
Experiment: determine # of photons/sec in a light
beam |
Electrostatics; lines of equipotential |
Thermo; PV
diagram |
Mechanical
power of ski lift |
||
|
Mechanics
– friction |
Mechanics
– energy & vertical circles |
Electron
moving through E & B fields |
Induced
variable current |
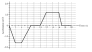
Calorimetry - GRAPH |
Standing
waves in pipes |
Wave-particle duality of radiation and matter |
||
|
This
year’s free-response section contained two-parts:
Part A contained five “major” questions and seven
“minor” questions. |
||||||||
|
This
year’s free-response section contained two-parts:
Part A contained five “major” questions and seven
“minor” question. |
||||||||
|
This
year’s free-response section contained two-parts:
Part A contained five “major” questions and seven
“minor” question. |
||||||||
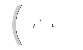




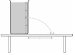







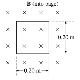

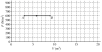


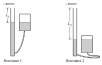

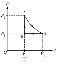


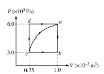



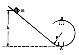
 B
and E fields on proton
B
and E fields on proton

 submarine
window as mirror, lens
submarine
window as mirror, lens


 upward
acceleration, tension in cables
upward
acceleration, tension in cables